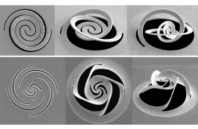
Nanokirigami has taken off as a field of research in the last few years; the approach is based on the ancient arts of origami (making 3-D shapes by folding paper) and kirigami (which allows cutting as well as folding) but applied to flat materials at the nanoscale, measured in billionths of a meter.
Now, researchers at MIT and in China have for the first time applied this approach to the creation of nanodevices to manipulate light, potentially opening up new possibilities for research and, ultimately, the creation of new light-based communications, detection, or computational devices.
The findings are described today in the journal Science Advances, in a paper by MIT professor of mechanical engineering Nicholas X Fang and five others. Using methods based on standard microchip manufacturing technology, Fang and his team used a focused ion beam to make a precise pattern of slits in a metal foil just a few tens of nanometers thick. The process causes the foil to bend and twist itself into a complex three-dimensional shape capable of selectively filtering out light with a particular polarization.

 (585) 768-2513
(585) 768-2513