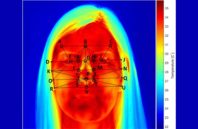
Researchers around the world are using infrared (IR) cameras to capture and record temperature variations on the skin for medical diagnostic purposes. By analyzing the images, researchers glean information on metabolic and vascular activity to recognize abnormal changes in physiology.
Thermal imaging is used to study a broad number of diseases where skin temperature can reflect the presence of inflammation in underlying tissues or where blood flow is increased or decreased due to a clinical irregularity. Currently, many physicians use thermal imaging cameras to detect a number of medical conditions, such as arthritis, repetitive strain injury, muscular pain, and circulatory problems.

 (585) 768-2513
(585) 768-2513