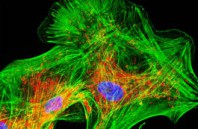
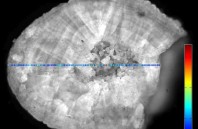
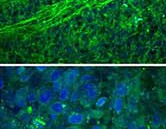
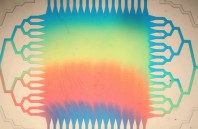
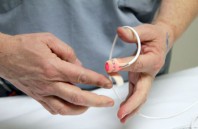
An international team of physicians and medical school students demonstrated in vitro a new quantitative microscope technology based on stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) that could allow surgeons to distinguish normal brain tissue from tumors in real time. The new technique,...
Read more
Laser-Based Microscopy for More Accurate Brain Surgery

 (585) 768-2513
(585) 768-2513